Hi all,
I’ve jotted down what I think are the most important variables for an investor to consider when exploring investment opportunities in the Indian IT space. You can also read this as an article on substack named “allthingsinvesting.substack.com”.
The focus is on qualitative aspects of a “typical” IT services business. I’ve not included businesses that offer IT Products and niche services. That is a topic for some other day.
Right at the onset let me say that I’ve learned a lot about this topic from various sources including Dr Malik’s blog, credit rating reports, Valuepickr threads and SOIC’s IT webinar. I highly recommend you check them out.
Please note that I have owned positions in a few of the businesses mentioned in the article since a long time. This is not an investment advice. I am not a registered advisor, please conduct your due diligence.
Current state of affairs
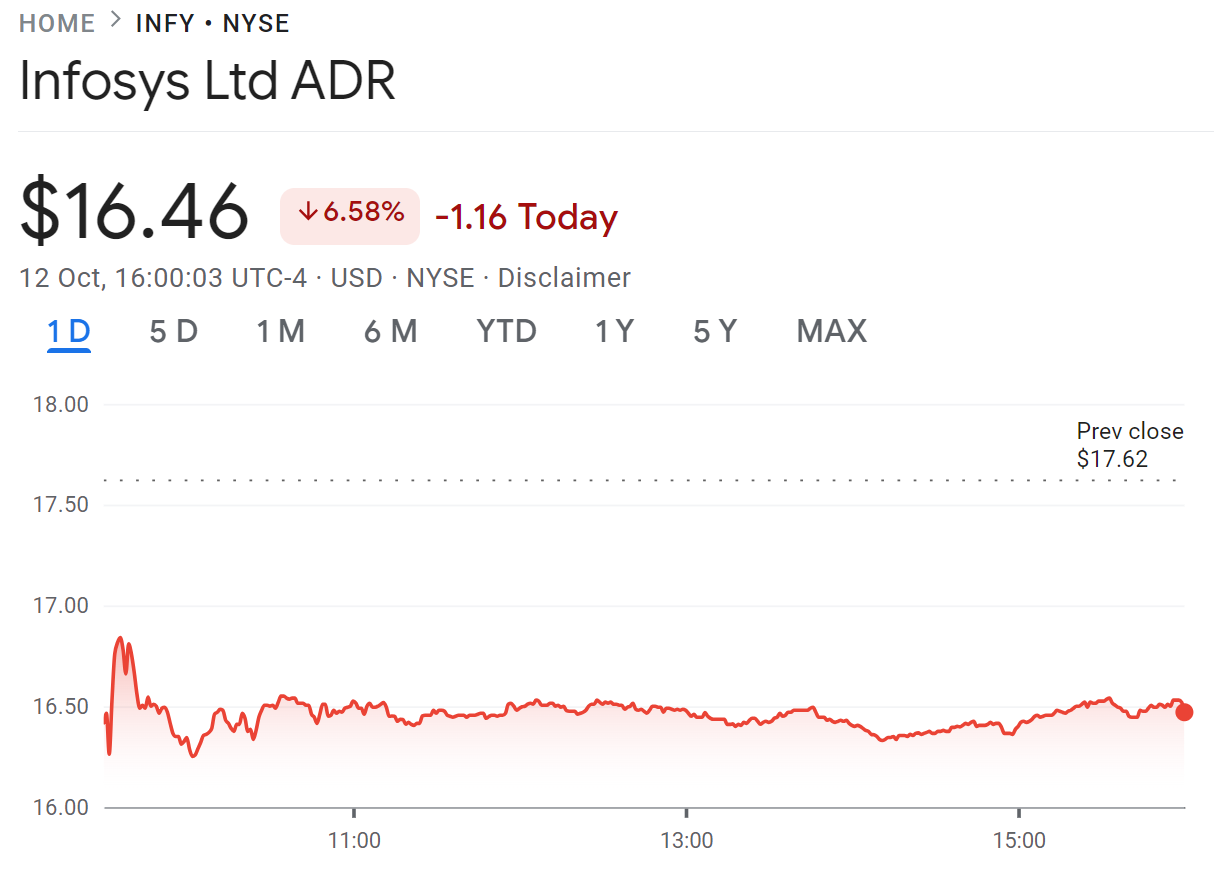
As I write the article on 12th Oct’23, the quarterly results of Infosys and TCS are out. The common theme is almost flat revenue growth, growing attrition and constant margin pressure. As a result, the market reacted and Infosys ADR (Infosys shares listed in the US) is down 6.5% in a single day!
So is it worth spending time on this topic?
Yes, I think the best time to study a business is when it is going through challenges. Once the key variables of such a business are understood, it becomes easy to track and check if there are indications of the challenges receding. Hopefully, some of these businesses will become an opportunity down the line.
So, let’s jump right in!
Key Variable: Domain and context knowhow
Importance of the variable:
Clients usually start by first outsourcing non-critical business process work to an IT service provider. As the service provider gains a deep understanding of the domain and the specific client’s way of doing business, gradually the critical business processes get outsourced. Hence, an IT service provider that carefully leverages years of experience, gains the upper hand in winning new contracts related to the client’s critical business processes.
What does it impact: Revenue
Positive impact on revenue due to the enhanced ability to win business over competition.
Where to find it:
Conference calls and media announcements can be monitored to check if the IT service provider is winning business-critical work or not.
Another way to check if the IT service provider has strong “productized services”. These are industry-specific nearly ready-to-deploy solutions that the provider can develop only after gaining deep domain expertise over time.
“Strategic accounts” are clients who offer work to the service provider directly instead of following the tender route. Hence a growing number of strategic accounts indicate that the IT service provider has deep domain expertise.
Examples:
- TCS started experimenting with blockchain with a use case around non-critical business processes such as corporate announcements. It will gradually move to more critical processes like loan securitization, card payments, etc. Management noted they will leverage domain and contextual knowledge.
- During a concall from Q1FY18 Infosys said it is working on “packet business solutions” created from 16,500 ideas it generated internally. This indicates Infosys may be able to deliver services in a shorter time compared to competitors, which any client values.
Key Variable: Diversified revenue sources
Importance:
Regulations and geopolitical events can cause different parts of the world and industries to grow at different rates. Events such as the financial crisis in the US and Brexit in the UK have forced clients to delay their IT expenditure. Having a large percentage of revenue from a specific geography becomes risky for an IT service provider. Similarly, overreliance on revenue from clients belonging to a particular industry is a source of risk. Most IT services companies derive one-third of their revenue from clients that belong to Banks, financial services and the insurance industry (a.k.a BFSI), which is a risk. Incidentally, the current decrease in revenue growth of most IT majors is due to a slowdown in BFSI clients in the US.
What does it impact: Revenue
The higher the spread of clients across geographies and industries, the more stable the revenue.
Where to find it:
“Revenue by Geography” and “Revenue by Industry” data are disclosed by companies quarterly and annually. A trend of increasing revenue diversification is desirable.
Example:
Mastek is an IT service provider that relies heavily on public sector clients from the UK and EU for business. Till 2022, 68% of the revenue was generated from the region, which the provider brought down to 62% by FY 2023. A credit rating report by ICRA highlighted the reliance on a specific geography and a specific industry as a challenge.
Key Variable: Having an entire bouquet of services
Importance:
Clients prefer an IT vendor that offers end-to-end services right from consulting, application development and management and product engineering to enterprise application management along with newer services such as data analytics, cyber security, cloud migration, IoT, etc. That’s because managing fewer IT vendors is simpler and clients can then focus on their core business.
What does it impact : Revenue
Large IT services businesses such as Infosys, TCS, Wipro and others leverage this aspect quite well to sustain customer stickiness, win large contracts and get opportunities to cross-sell other services. So, offering end-to-end services improves the chances of generating high revenue growth.
Where to find it:
Most companies claim to offer a wide array of services. It is difficult to identify gaps in service offerings. However, research reports and concalls help. So, unless I am looking at a niche IT service provider such as Cyient Ltd, checking the scope of services offered on the provider’s website, via industry-connect and research reports is important.
Example:
TCS’s CEO in Q4 FY18 noted that offering “full service” has been their key strategy.
Key Variable: Attrition
Importance:
Quite simply put, employees are the “raw material” of an IT service provider. Hence attrition may result in missed project deadlines, reduced quality of work and ultimately hamper client experience. Furthermore, it needs time to hire and train an employee to backfill the original position. While one cannot avoid attrition altogether, tracking management commentary on how they plan to keep it under check and if they are successful in doing it is key.
What does it impact : Cost, Future revenue
High attrition results in high employee costs (urgent hiring) in the short term and more severe issues in the long term.
Where to find it:
Most companies disclose attrition data quarterly and annually. A trend of declining or stable attrition percentage is a positive sign.
Key Variable: Type of contracts
Importance:
Typical types of contract IT service providers work with are fixed price and time & material (T&M). T&M contracts are where the client pays by the hours billed. This type of contract is safe for an IT service provider since issues like delays and extension of scope can be managed better as the client bears the cost. However, T&M also have lower margins compared to fixed-price contracts.
What does it impact: Margin
For a large IT service provider, a trend of increasing fixed-priced contracts is a positive sign as it indicates a better margin assuming they deliver the work without hiccups.
Where to find it:
Sometimes companies disclose data on the type of contracts quarterly and annually, otherwise, concalls can shed more light.
Example:
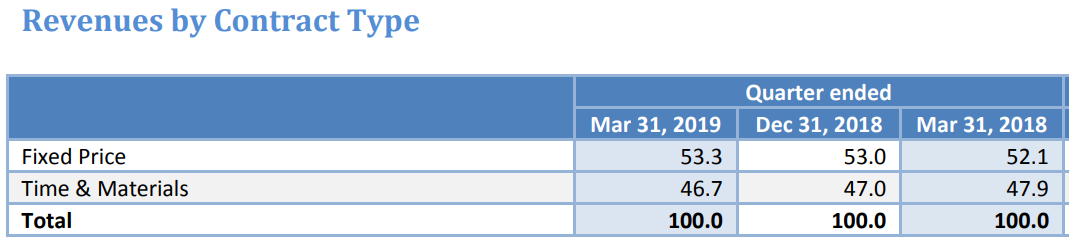
Infosys used to provide a breakdown of revenue by contract type till Q4 FY19. However, they’ve stopped disclosing it now.
Key Variable: Employee utilization
Importance:
This one is straightforward. For an IT service provider staffing employees on billable projects is important to generate revenue. At the same time, having some employees without a billable project is also needed to showcase the ability to deliver new projects quickly. During tough times such as FY 23, IT service providers choose to slow down hiring and focus on improving utilization levels.
What does it impact: Margin
Where to find it:
Most companies disclose utilization data quarterly and annually.
Example:
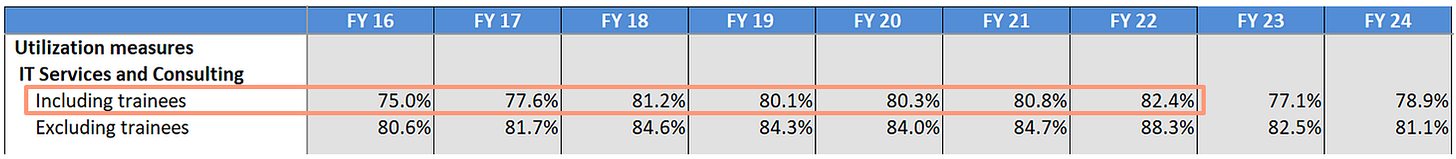
Infosys has shown good improvement in employee utilization from FY 16 to FY 22. The more recent utilization numbers are poor in comparison.
Key Variable: Onsite vs offshore mix and pyramid management
Importance:
Having employees in the client’s geography such as the US is expensive. However, it is convenient to coordinate and gain visibility of potential projects. Hence IT service providers try to maintain a balance between onsite and offshore mix.
For an IT service provider, keeping the pyramid flat is beneficial. It means having higher employees at lower levels and fewer at top levels. Both these variables are ways to control costs.
What does it impact: Margin
A not-so-well-established IT service provider may have to maintain a high percentage of employees in the client’s geography. So, a declining trend of onsite mix suggests that clients trust the provider’s capability of delivering work from India.
Where to find it:
Onsite mix data is usually disclosed quarterly and annually. For pyramid management, listening to quarterly concalls helps.
Example:
Infosys has improved its onsite mix over the years. However, it must be noted that its sub-contractor cost (mostly temporary on-site employees) has gone up.
Key Variable: Alliances and acquisitions
Importance:
For an IT services provider, to stay relevant, it is important to make sensible alliances and acquisitions to get niche talent, enter new geographies and develop new capabilities. During the last 5 years, IT service providers have made a lot of acquisitions in blockchain, analytics, IoT, customer experience and recently generative AI space.
Similarly, they’ve also made huge efforts to get employees certified on cloud, security and ERP tools. Having a large pool of certified workforce improves the chances of winning contracts and getting referrals from partners.
However, since not every effort succeeds only a few of these initiatives end up contributing meaningfully.
What does it impact: Revenue
Where to find it:
Annual reports and media announcements are a good source to track this variable. If one has limited time, listening to concalls will help since other analysts usually inquire about such developments.
Example:
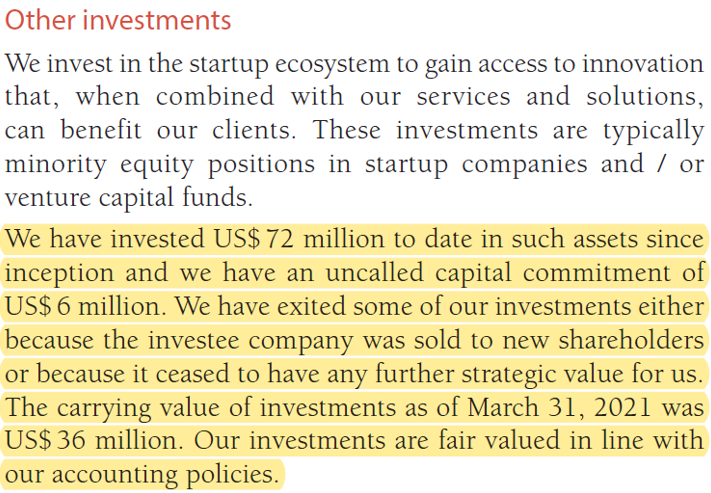
Infosys has an “Infosys Innovation Fund“ which identifies and invests in promising start-ups that can benefit Infosys. By FY 21, Infosys had invested $72 mn which became $36 mn after booking minor profits. Even though the outcome may not be impressive, in my opinion, investing a small portion of profit by spreading the bets across emerging technologies is a prudent strategy instead of missing out on opportunities.
There are a few other variables such as managing currency risk, book-to-bill ratio, maturity of systems and processes, etc. Looking through financials for any irregularities is important too. However, I am certain one can assess an IT service provider quite well by tracking the key variables mentioned above.
Let me know what you think.
Cheers!
Mahesh