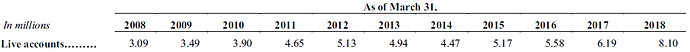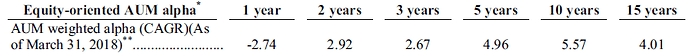Story
HDFC AMC is the largest asset management company in terms equity-oriented AUM and second largest AMC in terms of overall AUM. Its focus is on mass affluent consumers who are increasingly investing in equity markets as a form of long term investments in addition to traditional investment options like bank deposits and real estate. HDFC AMC is thus a direct play on financialization of savings in India.
As of March 31, 2018, company served customers in over 200 cities through pan-India network of 209 branches and a network of over 65,000 empanelled distribution partners across India, consisting of Independent financial advisors, national distributors and banks.
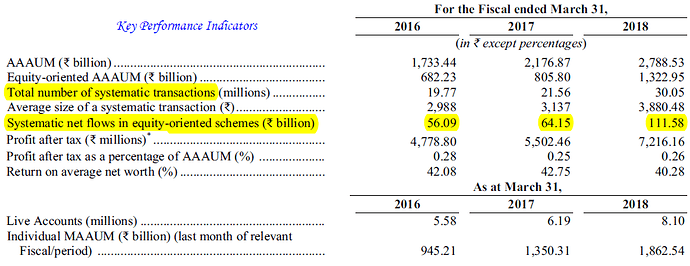
Key Performance Indicators
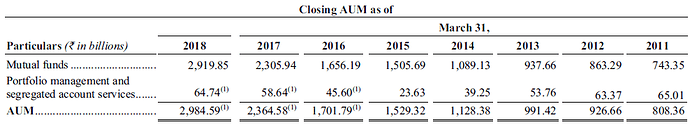
Table below shows the assets under management for last 7 years.
Source : IPO Prospectus
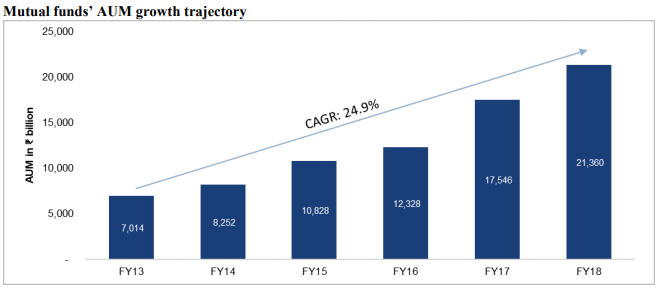
Company’s AUM has grown at a CAGR of 24% over the last 5 years, in line with industry but its equity-oriented AUM has grown at a faster rate of 37% over the same period. Majority of the assets are managed as mutual funds while AUM of PMS and other services is negligible. Company aims to serve mass affluent customers using mutual fund route rather than HNIs using PMS, AIF or other services.
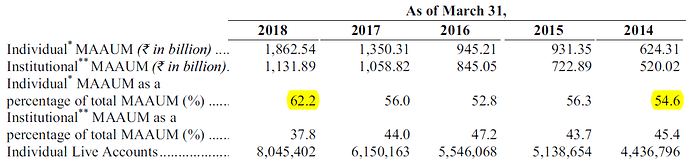
Over the last 5 years, share of AUM from individuals has steadily increased from 55% in 2013 to 62% in 2018. Table below shows break up of AUM by catagory of investors and number of individual investors served by the company.
Source : IPO Prospectus
Source : IPO Prospectus
As the table above shows, number of individual investors investing in mutual funds has steadily gone up over last 5 years. This trend is expected to continue.
Company offers equity, debt, liquid, index funds, ETFs and closed end funds. Over the years % of assets invested in equity oriented schemes have made up a larger share of total AUM. Table below shows annual average AUM by type of asset class.
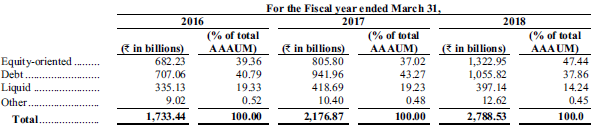
Source : IPO Prospectus
Company sources its customers using independent financial advisors, national distributors, and banks. A growing number of customers are investing directly with the AMC and AMC is passing on the cost savings to the cutomer in the form of low expense ratio. Following table shows breakup of AUM based on source
| Source of AUM | Total AUM | Equity Oriented AUM |
|---|---|---|
| IFAs | 28% | 39% |
| National Distributors | 21% | 24% |
| Banks | 17% | 19% |
| Direct Plans | 34% | 18% |
Source : IPO Prospectus
Although historical data is not available about direct plans, I feel higher proportion of direct customers will be beneficial to both AMC and customers.
Company has been offering mutual funds for more than 25 years and many of the company’s flagship schemes have generated strong track record. Table below shows some of the popular equity funds.
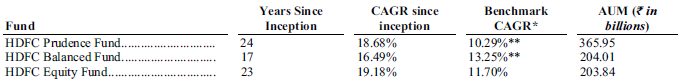
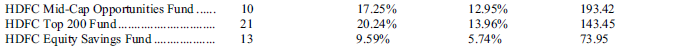
Source : IPO Prospectus
Company has also demonstrated its skill in managing large amount of funds and beating the benchmarks consistently. Table below shows alpha (excess return over benchmark) generated by company’s schemes.
Source : IPO Prospectus
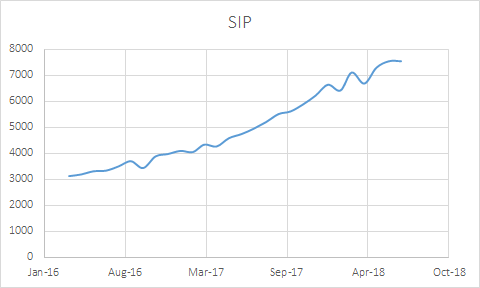
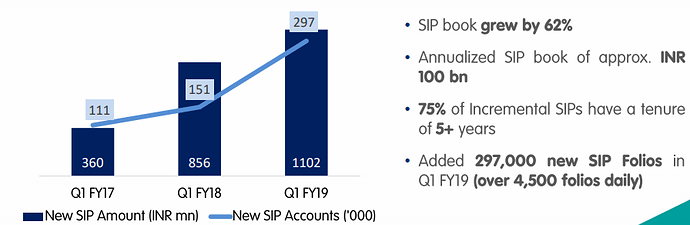
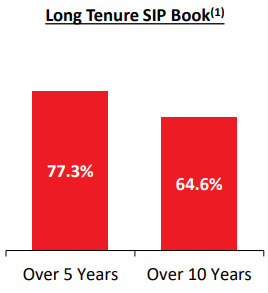
Systematic Investment Plans
SIP is a disciplined, risk mitigating and a convenient way to invest in mutual funds regularly. Many of company’s customers generate monthly surplus that they can conveniently and automatically invest in mutual funds. It provides a stable source of funds to the company. SIPs have been gaining in popularity over last 2 years and this trend is expected to continue. Table below shows trends in SIP.
Source : IPO Prospectus
Financial Statement Analysis
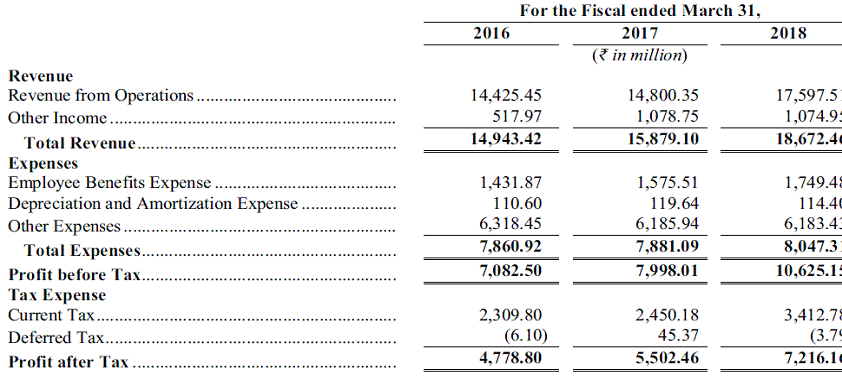
Income Statement
Company has been able to grow its top line and bottom line by a CAGR of 19% over the last 5 years with little volatility even when equity markets have been volatile over this period. Company’s AUM is linked to market but incremental sales has more than offset drop in market value of its AUM. This trend is also likely to continue provided volatility remains low.
Company’s major expenses are employee costs and business promotion expenses (which are included in other expenses). Expenses are more or less constant so company will see operating leverage as its size grows over time. Employee costs as a % of sales have been declining for years.
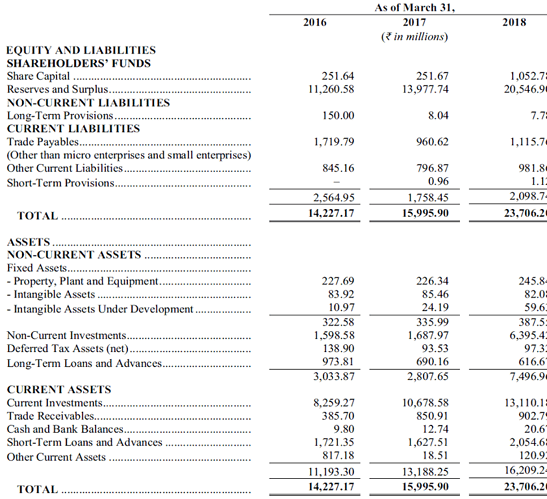
Balance Sheet
Company has a clean balance sheet with no debt and low receivables. This business does not need fixed assets and most of the company’s assets are investments, which are invested in its own funds. Unlike Reliance Nippon Life AMC, there are no interoperate deposits.
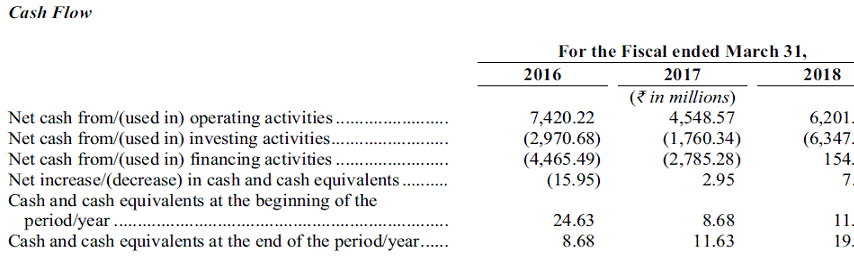
Cashflow
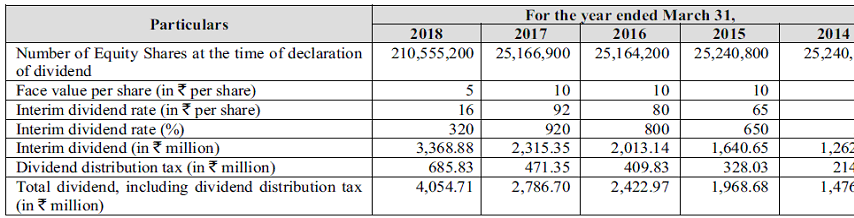
Company generates enough cash to grow the business and still has enough money left to pay 50% of profits as dividends.
Dividend policy.
Company has regularly paid dividends and is expected to pay 40-50% of profits as dividends given its high profitability and reinvestment requirements.
Profitability
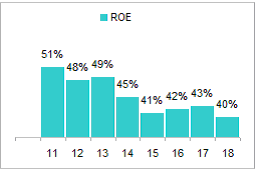
Company has consistently generated ROE in excess of 40% over last 8 years.
Valuation
Due to its high dividend payout ratio, I have used dividend discount model to value the company. Assuming a growth rate of 12% over next 10 years and a gradual slow down to 8.5% over next 10 years and a discount rate of 10.8%, fair value works out to be approximately Rs 1450 vs current market price of 1750. Stock is approximately 20% overvalued. However, given its long runway, investors are willing to pay next year’s price today.
Investment Rationalle -
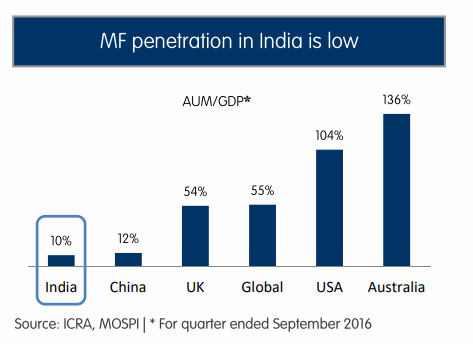
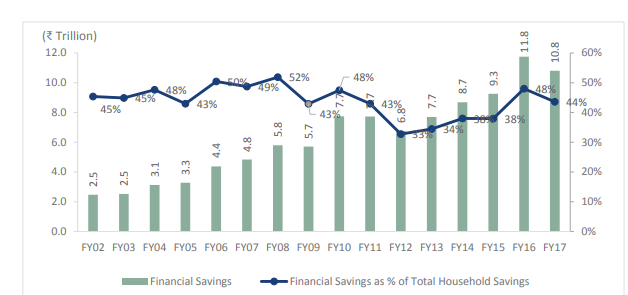
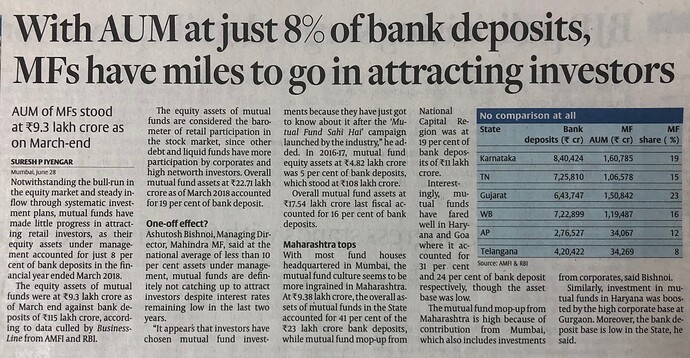
Long runway - Popularity of equities as asset class is growing in India due to better awareness, poor performance of other traditional assets like real estate and improving governance level both at corporate india and capital markets. However, equities only form a small % of total household savings in India. Mututal Funds is a popular way for masses to invest in equities as most investors will not be able to build their own portfolio.
Brand Name - HDFC has a strong brand name in India and it will help the company grow its AUM and pay less commission to distributors.
Invisible Revenue - I couldn’t find a better name for this but the mutual fund customers do not even realize how much they are paying to the AMC. This is perhaps one the few industries where customers aren’t even aware of what they are paying. This is a truly win-win situation. Customers get a higher return on their investments than all other alternatives they have and AMC gets revenue without even sending a bill to the customer.
Growing consumer franchise - Company’s proportion of AUM from individual customers is growing as a % of total AUM. This should help in reducing pricing pressure (as institutions are likely to bargin for a lower price), reduce churn as individuals are less likely to switch AMCs often and build a strong loyalty that might get passed down generations.
Better understanding of Indian investor - Multinational AMCs haven’t been able to scale in India even though they have been here for a while. Only Franklin Templeton is in top 5. Indian AMCs have better understanding of Indian investors, capital markets, distributors and regulators than MNCs.
Scarcity Premium - HDFC AMC is one of the only 2 AMCs currently listed in India. The other AMC is Reliance Nippon Life AMC. Compared to Reliance Nippon Life AMC, HDFC has better growth, more individual customers, higher % of equity AUM and better corporate governance. All these factors will result in higher valuation.
Risk factors:
-
Market risk - Company’s revenue is linked to AUM which in turn is linked to level of equity indices and interest rates. During bear markets, AUM may drop, new investors may not join and revenue can drop while costs will largely remain constant. This can result in a sharp drop in profits. Over the last few years, new sales have more than offset drop in average annual AUM during bear markets however there is no assurance that such trend will continue.
Debt funds form majority of AUM. While expense ratio of equity funds is stable, expense ratio charged to debt varies based on market conditions and competition. In case of sharp interest rate rise, company will have to drop expense ratios on debt funds. -
Concentration Risk - A small number of schemes represent a significant portion of AUM. As on March 31, 2018, top six equity-oriented schemes constituted 79.1% of total equity-oriented AUM and top six debt schemes constituted 65.5% of total debt AUM.
-
Alpha risk - Company’s funds may not be able to beat their benchmarks and may be be rated low on their performance by rating agencies. Such ratings have significant impact on sales. Historically, company’s funds have beaten their respective benchmarks but world over mutual funds have trouble beating their benchmarks. Company’s equity-oriented AUM is growing faster than overall market cap of indian equities so company may have trouble beating benchmark with a higher AUM base.
-
Risks from Passive Funds - Over last decade, passive funds have gained popularity around the world because actively managed funds have not been able to beat their respective benchmarks. In India, passive funds are not very popular as active funds have done well and are sold by distributors who are unlikely to push passive funds due to low commissions. However, passive funds have significantly low expense ratios so growing popularity will dent profitability of AMCs.
-
Mis-selling Risk - Over the last 2-3 years many investors have invested in mutual funds for the first time primarily based on advice from their financial advisors. These advisors are paid a commission by the AMCs and may have mis-sold funds to investors who do not understand risks of investing in these funds. Such mis-selling although has resulted in short term boost to the sales, can have long term negative impact on the growth of the industry.
-
Regulatory Risks - AMCs earn their revenue by charging expense ratio to funds. SEBI has capped the rate at which such expenses can be charged. Expense ratios in India are already among the highest in the world and SEBI is likely to reduce the cap over time. HDFC being the largest AMC, will be able to mitigate this risk due to its scale.