At its simplest, biotechnology is technology based on biology - biotechnology harnesses cellular and biomolecular processes to develop technologies and products that help improve our lives and the health of our planet. We have used the biological processes of microorganisms for more than 6,000 years to make useful food products, such as bread and cheese, and to preserve dairy products.
Bioeconomy :
The bioeconomy is the knowledge-based production and use of biological resources to provide products, processes and services in all economic sectors within the frame of a sustainable economic system
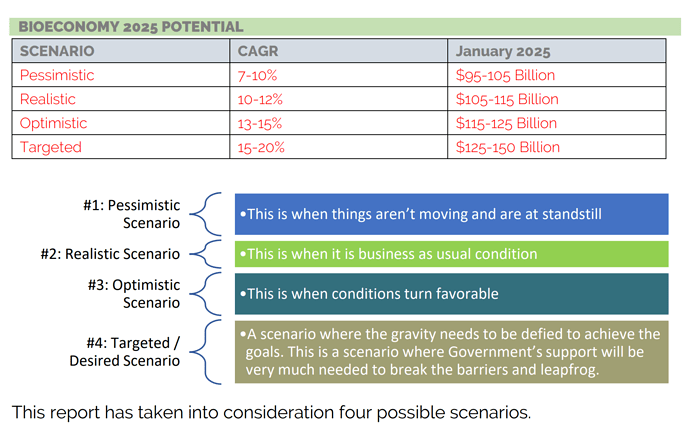
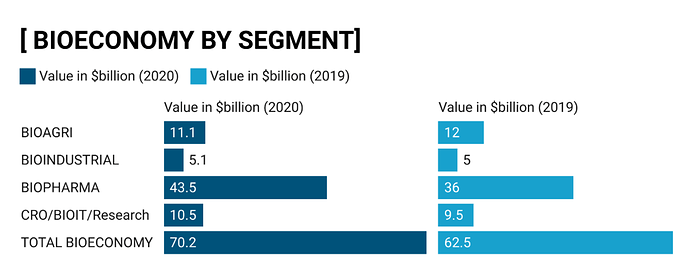
- Indian bio economy size in 2020 is $70.2 Billion (Link to source Bioeconomy report 2021 - A must read)
- By 2025 it would be worth of $100 - $150 bllion
- The share of BioEconomy in the national GDP too has been rising steadily in the last few years. The share now stands at 2.7 % against 2.2 % in 2019
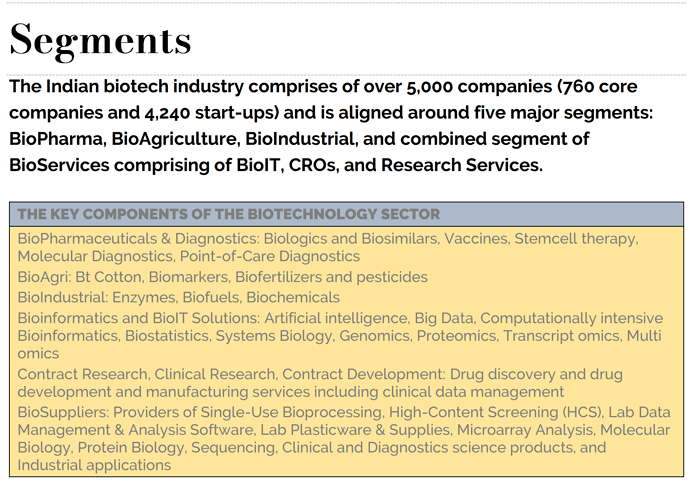
- Total 840 biotech startups in 2020 to take the total numbers to 4,237. About 61 % of these
startups are in the biomedical segment including biopharma, medical technologies and diagnostics
Segments in Bioeconomy
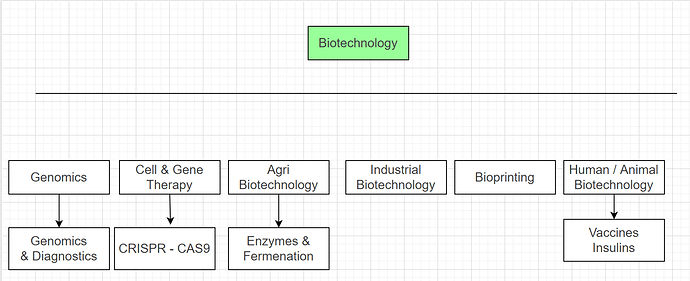
Biotechnology is a big ocean so here I am listing down some important building blocks.
Genomics & Diagnostics
What is a DNA, Gene and Genomes ? Watch a short video here
DNA
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It is a chemical made up of two long molecules. The molecules are arranged in a spiral, like a twisted ladder. We call this the double helix structure. There is DNA in the nucleus of every cell. DNA carries genetic information. It has all the instructions that a living organism needs to grow, reproduce and function.
Genes
Genes are short sections of DNA. Genes carry information for particular characteristics, such as ear shape or eye colour. Different sets of genes carry information for different characteristics. There are many genes in a chromosome.
Chromosomes
In a cell nucleus, DNA is organised into coiled strands called chromosomes.
Humans have 46 chromosomes in each cell. The fruit fly has only 8 chromosomes and is often used to study patterns of inheritance, while red king crabs have a whopping 208!
Half the chromosomes are inherited from one parent and half from the other. As humans, therefore, we have 23 chromosomes from each parent.
This explains why organisms can share characteristics from both parents. A child, for example, might have red hair like their dad and long fingers like their mum.
A genome is an organism’s complete set of genetic instructions. Each genome contains all of the information needed to build that organism and allow it to grow and develop.
Example of a disease that are caused by DNA mutations
Sickle cell disease is an inherited disease caused by defects, called mutations, in the beta globin gene that helps make hemoglobin. Normally, hemoglobin in red blood cells takes up oxygen in the lungs and carries it through the arteries to all the cells in the tissues of the body
Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as proteins, applying molecular biology to medical testing. In medicine the technique is used to diagnose and monitor disease, detect risk, and decide which therapies will work best for individual patients,[1]2 and in agricultural biosecurity similarly to monitor crop- and livestock disease, estimate risk, and decide what quarantine measures must be taken
Basically Molecular diagnostics are the techniques used to identify the defects in the genes.
Treatments
Cell and Gene Therapy (Most of the research is on Oncology, which targets a specific faulty gene and repair )
References / Cures by using Cell Therapy :
First UK patient receives stem cell treatment to cure loss of vision
Some of the proven treatments in India
LV Prasad eye care is one of the institute working on this
Gene Therapy
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) - Gene therapy is a game changer for our son
End of Part 1
Part 2 :
Bioprinting (Regenerative Medicine)
This is an extension of 3D printing, where we can think of building organs in the Lab ( Something like meat produced (cell cultured) in the lab
Bioprinting human tissues (this can reduce the dependency on animals for drug trials )
How Scientists Are 3D Bio-Printing Human Organs
Agri Biotech
Gene editing in Crops by using CRISPR - CAS9 . we can rely on these and produce crops with more nutrition values many more advantages.
This is slightly different to GMO crops where a foreign gene is induced , a good research paper. ijerph-17-02935-v2.pdf (2.0 MB)
A very interesting thing is there is open MTA framework (it is like open source software where anyone can take the software and use it for non profit purposes and pay only when one modifies and resells it ) , this is a right step to encourage and more people to participate in this research in a collaborative way
A good webinar on : Agricultural Biologicals Today & Tomorrow: Opportunities and Challenges
I think Sumitomo and Coromondal ( I am sure many others are producing bio pesticides ). Sumito Chemicals india works with their parent subsidiary Valent
Natco is working on similar lines
Human and Animal Biotechnology
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Antibody-drug conjugate - DCAL and Piramal is specialized in this
- Peptides
- Vaccines
TBC…
@adminph2 , this thread is under construction , I am keep on editing the content, please bare with me.