Hi, below are my notes from D-Mart Analyst/Investor meet 2018 held this week. Note that this does not cover all points, but is only a summary of key points
Key Highlights
1.Addition of Stores
a. While refusing to give out a number for annual store additions, management indicated that it can comfortably add 20-25 stores annually
b. Targeting over 30 store addition annually will be a big challenge
c. It takes between 24-30 months from identifying a location and getting the store operational
d. Historically, D-Mart has focussed on Owning its stores rather than leasing. However off late, it is also adopting the leasing model
e. Profitability for leased store is better than owned store
f. Preference for owning comes from the fear that once a store is established in a micro market, lease renewals will give undue bargaining power to the landlord and thus increased lease costs are likely to hit margins 10-15 years later when the lease for current stores expires
g. A lot of time and effort is given on getting the location right, company believes in getting the best location even if it is coming at a premium
h. High cost of Real Estate prevents the company from aggressive expansion in metros like Mumbai; there still are some pockets in the suburbs where the model works
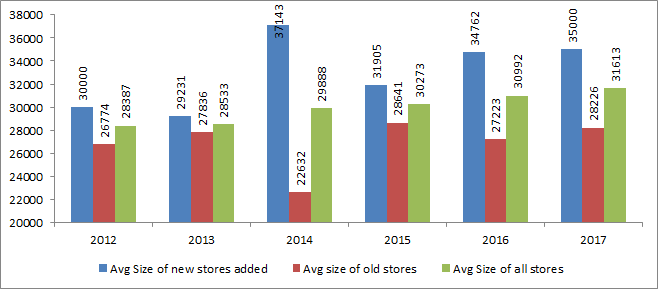
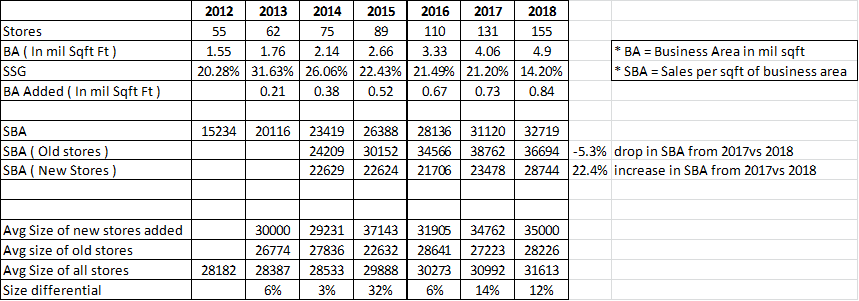
i. Revenue per sq.ft for D-Mart stands at Rs. 2,726 psf pm on average
-
This figure is higher for stores in Mumbai and lower for stores in Tier III & Tier IV
-
However, profitability per store is more or less similar (Refused to give numbers)
-
SSG in Mumbai would be low, but sales per square foot is high ensuring margins are protected
j. Company is expanding in clusters. Prefers this approach vs venturing into unchartered markets due to limited management bandwidth
k. All 155 operational stores of the company are profitable and it has never closed a store
2. Growth of existing & new stores
a. Investors had plenty of questions on tapering Same store Sales Growth (SSG)
b. Management believes that SSG is a function of many things and thus complex to predict
-
For Eg, a store opened in Malad continued to grow at 20% for many years until they opened a store in Mahavirnagar, Kandivali
-
SSG for Malad dropped substantially but D-Mart was able to capture higher market share combined
c. For old and mature stores, company guided of SSG to be in line with inflation. Younger stores will have high growth rates until their base becomes high
d. Old stores at prime locations will continue to grow (Like the 1st store in Powai)
3. Pricing
a. D-Mart is extremely confident of delivering on their promise – Lowest Price, every day
b. Has a proprietary algorithm in place which scans product prices across competitors (including Big Basket, Amazon Pantry etc.) and sets the product prices at D-Mart stores
c. Some of the competitors have become aggressive with discounting to compete with D-Mart. The company’s response is “If our competitors drop prices, we will drop our prices further”
d. The company will do everything possible to ensure that it is able to offer a product to the customer at the lowest price
e. If the sales velocity of a product is low, the prices are dropped immediately to clear inventory
f. On asked what is their differentiating factor v/s competition, CEO said D-Mart stores are extremely crowded, AC is poor, Merchandise Display is not the best; despite this people come and shop at D-Mart only because it offers best value for money!
g. It does not wish to compete with Metro, Nature’s Basket and other such premium chains. They wish to continue catering to the value conscious consumers, which are plenty in India
h. Management believes inflation is good for its business as revenue inflation is always > cost inflation
- Wages are the highest impact on cost while other operating expenses like electricity etc. always grow lower than inflation
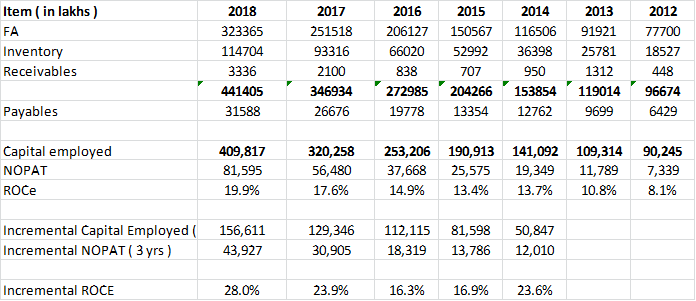
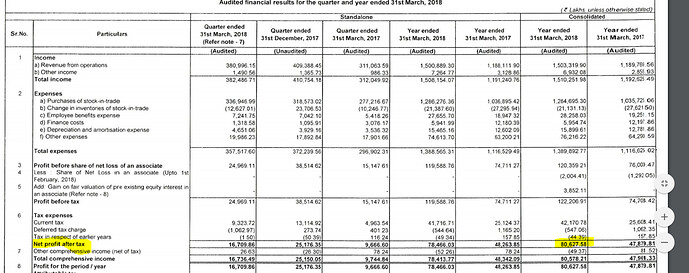
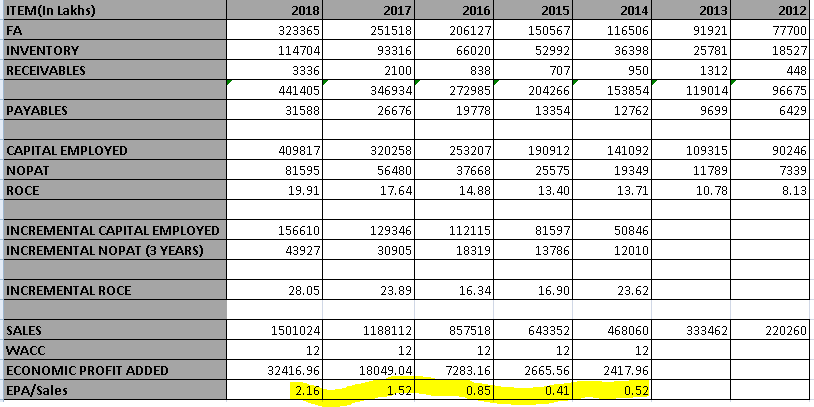
i. For FY18, D-Mart reported EBITDA margins of 8.9%
· It believes that any effort to further improve margins would be at cost of customers which the company would never want
j. Put in place Centralized procurement in the last 36 months – this was implemented category-wise. This has helped improve margins
4. Opportunity Size in Retail & competition
a. Retail spend in India was $616 bn is expected to be $960 bn by 2020 of which D-Mart is able to capture only Rs. 15,000 cr (~ $2 bn) in FY2018
b. Management believes Retail has enough space for everyone to co-exist and still make money
5. How does the company decide category-mix and what does it do to keep increasing sales?
a. Fundamental outlook of the company – Give a customer what it wants, even if it means you are making less money in short term
b. Maximum shelf space is allotted to the product that sells the most and not to the product that has highest margins
c. If you can’t compete in a category, don’t operate in it
-
D-Mart stores are known for not keeping fruits & vegetables in most stores
-
Fruits & Vegetables are sold by roadside vendors who have no establishment costs, pay no taxes and can afford to sell at prices which D-Mart can’t beat
d. Private Labels – Indian consumer wants the highest quality product, should be branded and it should be at the lowest cost
- Will take time to establish in this segment
e. Keep doing small improvements often, but don’t micro-analyse
6. On E-Commerce
a. “Do your job best, don’t focus on competition” – R K Damani
b. ‘D-Mart Ready’ is the company’s venture into online retail where customers can have grocery delivered to their home or have it picked up from a D-Mart Ready store (Kirana store- tie-ups)
c. Grocery as a category has been a laggard in e-commerce
d. With the advent of Walmart who comes with a grocery background in India, if there were to be a Price War in this segment in future, the losses of Amazon/Flipkart would be far higher than today
e. Cost-cutting in case of E-commerce players will hurt more than for Brick & Mortar stores
f. Currently, D-Mart Ready contributes less than 0.01% of total revenues (insignificant)
7. Incentives & Employee management
a. No targets are given to any employees as there are multiple functions contributing to the topline
- Eg: It would be unfair on a store manager being given a sales target and management deciding to open another store within 3-4 kms from that store which would affect the sale of that store
b. Instead, they have rigorous systems in place to evaluate performance of employees (Did not elaborate on this)
c. Store manager has the freedom to make changes as per discretion, but most stick to the tried & tested template
d. The top management sees itself as mentors to ensure that no big blunders are done and junior employees are encouraged to take decisions
Discl: Not Invested, only tracking

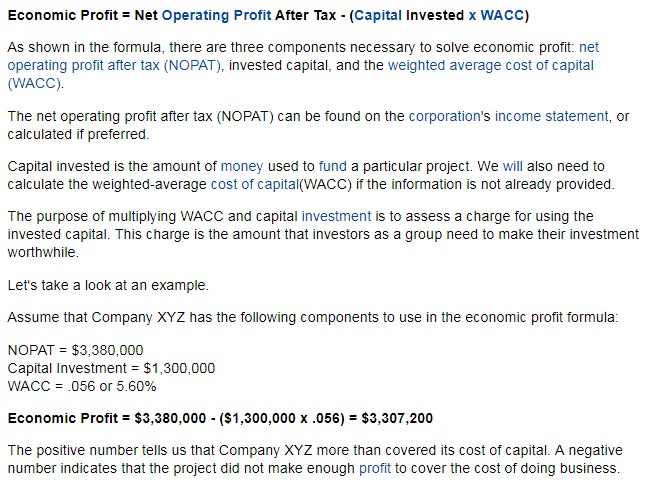

 How do we estimate the cost of capital?
How do we estimate the cost of capital?