Sharing my notes on astra microwave -
disclaimer - invested with no recent transactions
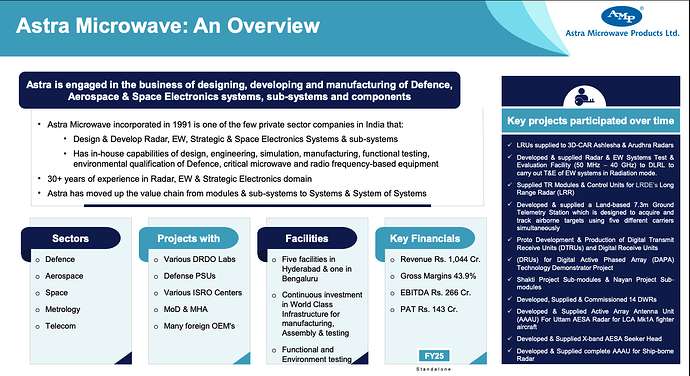
Astra microwave products is a manufacturer and designer of high performance Radio frequency (RF) and microwave modules, sub-systems and systems. It’s products find application in defense, space, meteorology, homeland security systems integration and unmanned ground vehicles and is steadily moving up from components/sub‑systems to full systems and solutions, especially in radars and weather applications.
what sets it apart?
Astra has over 30 years of deep domain expertise and DSIR-recognized research and development capabilities, with a team of more than 400 R&D staff with comprehensive in-house testing capabilities including MMIC (Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuit), digital, PCB (Printed Circuit Board), mechanical, and environmental testing across 6 facilities located in Hyderabad and Bangalore. Astra is one of the few private sector players in India that has the capability to develop and supply GaN & GaAs MMIC products upto 40 GHz.
The company has established long-term relationships with DRDO laboratories, DPSUs, and ISRO and are an approved production partner for multiple foreign OEMs including Elta, Elbit, Rafael, and Thales. Astra execute both BTS (Build-to-Specification) projects, which are high value-added contracts, and BTP (Build-to-Print) projects, which serve as capacity fillers.
History
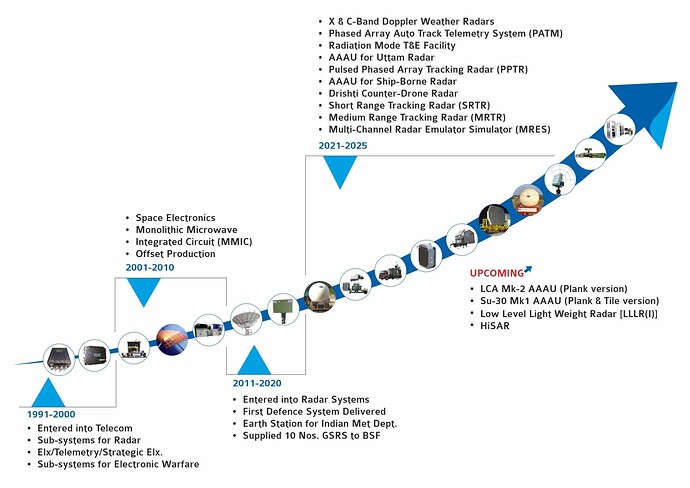
Astra was incorporated in 1991 in Hyderabad by a team of DRDO‑trained scientists in RF/microwave and digital electronics. Although the founders had defense in mind, the company’s first break came from India’s early-1990s telecom boom, which helped seed product development and cash flows. By 1993, Astra’s first microwave components and sub-systems were finding their way into DRDO radar programs, alongside early telemetry and strategic electronics work. To fund infrastructure, people, and test capability, Astra went public early listing on Indian exchanges in 1995. In 1997, it recorded its first R&D deliveries into a DRDO surface-to-air missile telemetry program.
Through the 2000s Astra deepened in defence and stepped into space. ISRO began awarding the private sector space‑grade work in the early 2000s, and Astra became a recurring supplier of on‑board RF sub‑systems and ground satcom/telemetry gear. Inside the company, it built a fabless MMIC design team (GaAs/GaN) to de‑risk critical RF devices and to shrink/modernise transmit‑receive modules - capabilities that would later prove important for AESA radar programs. It also kept investing in labs: EMI/EMC, environmental test, and multiple SMT lines across expanding Hyderabad units.
From the late 2010s into the early 2020s, Astra moved up the value chain from sub‑systems to full systems and integration. It broadened radar offerings (ground surveillance, coastal, weather) and meteorology/hydrology instruments, while commissioning a near‑field antenna test range in Bengaluru to qualify active phased arrays. In meteorology, Astra delivered multiple X‑ and C‑band Doppler Weather Radars and automated weather networks for IMD, and built a steady presence in wind profilers and hydrology stations.
Today the company has three production units and two R&D units that also include an exclusive space qualified facility. Astra today has an array of assembly and test facilities that include 3 Automatic assembly lines for PCBA assembly, Seven Class 10K and one Class 100K clean rooms, functional test infrastructure that extends from 30MHz up to 40GHz, in-house Environmental Test facilities including EMI/EMC facility and a first for any Indian Private Industry - Near Field Antenna Test Range (NFTR).
business segments
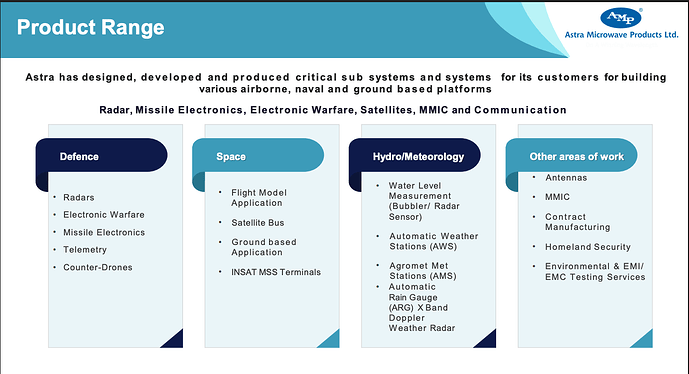
Defence
Radar electronics
Radar electronics involve systems that use radio waves for detecting, tracking and navigating objects. Advanced technologies like Active Electronically Scanned Array radars enhance detection capabilities and operational efficiency. These systems are critical in defence, aerospace, automotive (for ADAS features like adaptive cruise control), and infrastructure sectors.
The Indian radar market was valued at USD 230.3 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 20.62%, reaching nearly USD 1.4 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing defence budgets, modernised airport infrastructure and the expansion of civil aviation, with over 500 million air travelers expected in India by 2030. The sector is expanding due to advancements in radar technology, rising demand for surveillance systems and government initiatives promoting indigenous manufacturing.
The company has established itself as India’s leading private sector radar house with capabilities spanning from MMIC chip design to complete system integration, positioning it to capitalize on the expanding domestic and export radar markets.
some of the products in this segment -
- Active Antenna Array Unit (AAAU) - the first private company to deliver the Active Antenna Array Unit (AAAU) for India’s indigenous Uttam AESA radar used in the Tejas fighter jet and similar shipborne systems, enables detection, tracking, and missile/fire control.
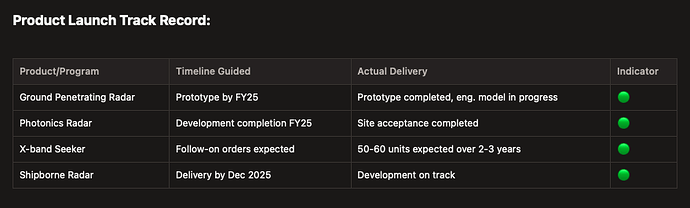
- X-band AESA seeker - Advanced radar “eye” fitted in missiles to guide them precisely to moving or hidden targets.
- QRSAM subsystems - Vital electronic subsystems (like radar electronics and RF modules) for India’s mobile air-defense Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile (QRSAM), enabling rapid detection and interception of aerial threats.
- counter UAS - anti-drone solution combining active radar detection, passive RF sensors, and multi-band jamming capabilities (including non-standard frequencies) with omni-directional coverage extending up to 5+ kilometers range.
- Shipborne Multi-Function Radars - Indigenous replacement for imported naval radar systems, providing 360-degree threat detection and tracking capability for Indian Navy vessels across different ship classes and operational requirements.
- Fire Control Radar Subsystems - Critical T/R modules, signal processing units, and RF front-ends for air defense fire control radars like ADFCR, enabling precise target acquisition and weapon guidance for Army air defense systems.
- Photonics Radar Subsystems - Next-generation radar technology utilizing photonics for enhanced bandwidth and performance characteristics, representing cutting-edge development in collaboration with DRDO for future radar architectures.
Electronic warfare
Electronic warfare (EW) involves the strategic use of the electromagnetic spectrum to detect, intercept, disrupt or deceive enemy systems while protecting friendly operations. It includes Electronic Attack (EA), Electronic Protection (EP) and Electronic Support (ES), with modern systems incorporating AI, jammers and directed energy weapons. EW is primarily used in defence (threat detection, secure communications), homeland security (counter-terrorism) and intelligence agencies (SIGINT/ELINT operations).
key products here
- Wideband & Ultra-Wideband Subsystems (0.5-40 GHz) - Critical RF front-ends for EW systems covering multiple threat bands, enabling simultaneous detection and jamming across the electromagnetic spectrum for naval, airborne and ground platforms
- DIFM (Digital Instantaneous Frequency Measurement) Receivers - High-speed receivers that instantly identify and characterize enemy radar frequencies, forming the core of radar warning receivers (RWR) and electronic support measures (ESM) systems
- Compact Microwave Receiver System (0.5-40 GHz) - Recently delivered to DLRL/DRDO in 2025, this wideband receiver provides comprehensive spectrum coverage for electronic intelligence (ELINT) and signal intelligence (SIGINT) applications.
telemetry
Telemetry is a critical technology for remote measurement and real-time data transmission, widely used in defence, aerospace, healthcare and environmental monitoring. In defence, it tracks missile and aircraft performance, while in healthcare, it enables continuous patient monitoring. Automotive industries use telemetry for vehicle diagnostics and environmental agencies rely on it for weather forecasting and disaster management. Astra supplies telemetry subsystems for platforms like the LCA Tejas and IJT aircraft.
Space
Astra Designs, develops and manufactures components and sub-systems used in ground-based modules and Slevel (on-board) modules. Astra have been among the key players for the development of sub-systems for India’s Radar Satellite & Geosynchronous Satellite program, Resourcesat, Megatropics and Cartosat for Indian space programs by ISRO. Astra has a order book of 239cr as of 1Q26 end from space sector. Opportunity size in this segment is close to 600crs till FY28.
key products here:
- Flight-qualified RF sub-systems (filters, amplifiers, receivers, antennas) flown on ISRO satellites (RISAT, GSAT, Cartosat, Resourcesat, Megha-Tropiques).
- SATCOM terminals and ground stations; 7.3m ground telemetry systems for ranges like ITR.
Astra has established a wholly owned subsidary by name astra space technology private limited to focus on space sector in a bigger way and taken steps to recruit people and assembly rooms for assembly and integration of small-sized satellites. astra has also formed a SPV with a leading leading defense PSU to bid for a specific space tender.
Active Programs & Recent Deliveries:
- Onboard digital signal processing system for satellite payloads (recently delivered - positions Astra to build complete payloads)
- Critical subsystems for DRDO/ISRO satellite programs: OTGR, Anvesha, SAMOOHA
- Multifunction pulse compression radar delivered to ISRO (site acceptance completed)
- Recent mission where Astra contributed 9% of payload value and 3% of overall satellite value
Meteorology & hydrology
Meteorology ensures precision measurement in manufacturing. Meteorological devices are essential tools for collecting and analysing atmospheric data, crucial for weather forecasting, climate research and various industrial applications. These instruments measure temperature, atmospheric pressure, humidity, wind speed and direction and precipitation. Common devices include hygrometers, barometers, thermometers, anemometers, and rain gauges. In sectors like aerospace, defence, agriculture and environment monitoring, the need for accurate, real-time weather data has grown substantially.
Hydrology on the other hand monitors water resources using sensors, GIS and real-time analytics. Astra’s components enable accurate data collection. The Company specialises in solutions for agriculture (irrigation planning), energy (hydroelectric dam management) and urban infrastructure (Smart water grids).
products by the company in this segment:
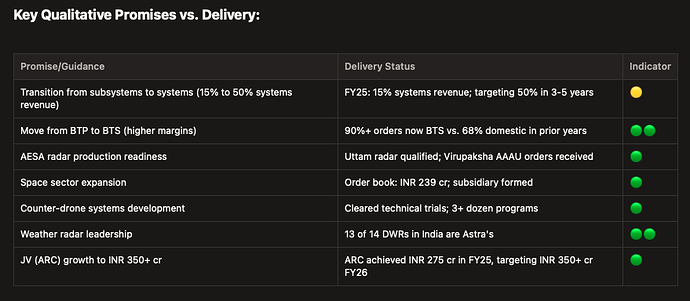
- Doppler Weather Radars (DWR) - X/C-band - Astra has delivered 13 out of 14 DWRs currently operational across India for IMD.
- Wind Profiler Radars - Advanced atmospheric monitoring systems that measure wind speed and direction at multiple altitudes, crucial for aviation safety and weather prediction
- Water Level Measurement Systems - Advanced bubbler and radar-based sensors for accurate water level monitoring in rivers, reservoirs, and groundwater systems
Management expects order book exceeding INR 400 to 500 crores from meteorology and hydrology segments within next 2 years with opportunities from MAUSUM program, Weather as a Service and some other programs.
Subsidaries & JVs
Joint ventures
Astra Rafael Comsys private Limited
Astra Rafael Comsys private Limited is 51:49 joint venture between Astra and Rafael Defense Systems Limited, Israel. Astra alone holds 50% in this venture. ARC is engaged in India in indigenous development, production and integration of high-end digital communication systems which includes a wide range of technologies and products like SDR, ESM and Cognitive Radio technology.
key products:
here’s a video to understand better : https://www.astrafaelcomsys.com/assets/vedio/bnetff1_.mp4
For FY26, management guides to ~INR 350+ crores revenue with PBT of 10% and an order book already INR 400‑plus crores, with visibility to secure close to $100 million across three major contracts before March ’26 and potential aggregate inflows of 800 crores.
subsidaries
Bhavyabhanu Electronics Private Limited : This is the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary that possesses state-of-the-art manufacturing and testing facilities addressing global standards.
Aelius Semiconductors Pte. Ltd: This is a fabless MMIC design house in Singapore that specialises in designing GaAs and GaN MMIC products. The Company utilises leading foundries worldwide for fabrication and utilises cutting-edge facilities for testing and packaging products.
Astra Space Technologies Private Limited: This is the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary engaged to carry on the business of design, development and integration of satellites, satellite pay loads, launching of satellites, and establishment of ground stations for satellite tracking. Management also noted that a leading defence PSU formed an SPV with Astra to bid a specific space tender.
What underpines my bullishness
Transition from a build‑to‑spec sub‑system supplier to a systems integrator/solutions provider
In the past when the company had no sectorial understanding, it focused on components and sub systems. In doing so, the Company gained an insight into building a sub-system from scratch; thereafter, it developed an insight into the manufacture of other sub-systems.
Now the focus of astra is to move from fabrication and assembly of sub-systems to complete systems. In FY25 company generated only 15% of its revenues from large and complex systems which it intends to increase to 50% in next three to five years, strengthening its margins and return ratios.
Strong Order Book & BTP vs BTS
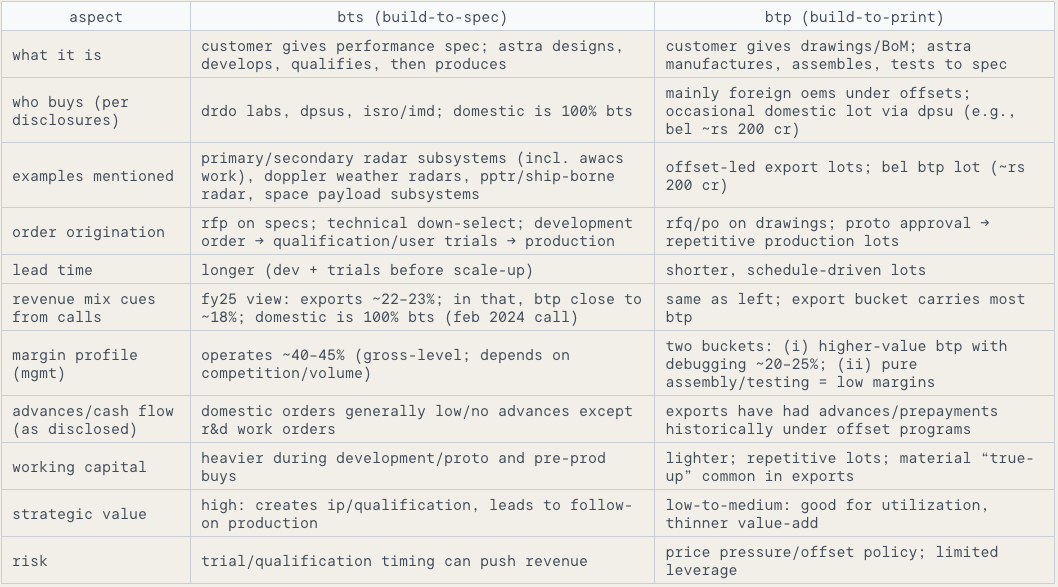
There are fundamentally two types of orders for Astra micro:
Build-To-Spec (BTS): customer gives a performance specification and then astra designs, develops, qualifies, and then produces the subsystem/system. BTS has a higher value add and provides better margins to Astra. Company here works with systems integrators like DPSUs (Defence Public Sector Undertakings) and others for commercialization of the products.
Build-To-Print (BTP): design is usually provided by the OEMs itself, so astra manufacture, assemble, test to the customer’s drawings with not much value addition and lower margins compared to BTS orders. Astra works with many foreign OEMS for producing their products in India under this mode for meeting their offset requirements with key customers including Elta Systems Ltd, ELBIT, Rafael, Thales.
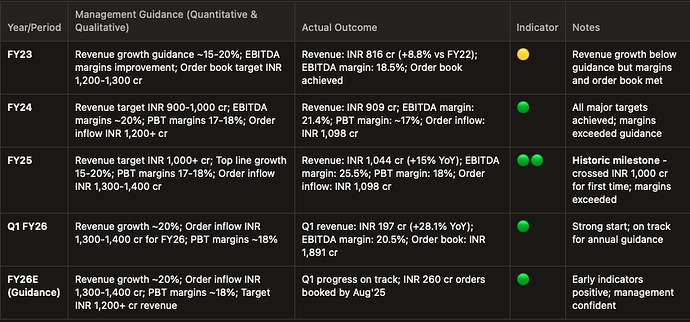
order book for astra stands at Rs 1,891 cr as of 1QFY26 (standalone), with 90% + of orders being BTS (higher value-add/margins). New wins included AAAU for LCA Mk‑2 and Su‑30 and radar sub‑systems for Akash Prime and VL‑SRSAM, plus weather radars and agro‑AWS for IMD. Management guided FY26 order inflow of Rs 1,300–1,400 crore, revenue growth near 20%, and PBT margins around 18%, with systems (radar/EW, counter‑UAS) as the growth engines.
Key programs and TAM
| Program/Opportunity | Estimated Astra Share (INR Cr) | Status | Astra’s Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| QRSAM (Quick Reaction SAM) | 1,700-1,900 | BEL order expected 4Q26 / 1Q27 | Key supplier of TRMs, receivers/exciters for radar + missile subsystems |
| Virupaksha Radar Program | ~2000cr over next 3 years | Development ongoing | AAAU is 55-65% of radar value; mgmt said more than twice our turnover when productionized |
| Uttam AESA Radar (Tejas) | Phase-1 orders expected FY26 | Selected partner for 130+ radars; 36 units/year capacity | |
| Project Kusha | - | Development stage | Key supplier of TRMs, receivers for radar subsystems |
| MAUSAM Program | 300-400 | Active participation | Delivered 13/14 installed DWRs; significant player |
| Counter-UAS Systems | 200-250 | Multiple RFPs active | Indigenous complete solution; >3 dozen programs |
| ARC JV (SDR/Electro-optics) | 800 | $100M pipeline visibility | One of 3 shortlisted for Army backpack SDR |
have they delivered in past?
red flags
- B2G risk : Revenue is dominated by Indian defence B2G programs where DRDO specs and L1 tendering drive awards. Delays in orders for subsystems remains a major risk factor
- Working-capital intensity : company has a high working capital cycle; this can force higher borrowings or equity raise for further growth
- Supply-chain risk: GaAs/GaN/MMIC and mil-grade parts are long-lead / export-controlled; shortages can delay builds or force redesigns.
- Execution/qualification risk: System-level programs carry higher integration risk