Background:
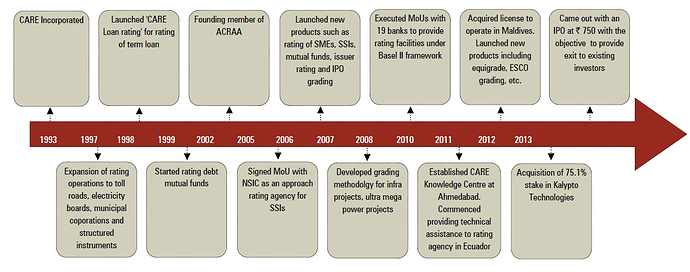
CARE is second largest Credit rating agency, promoted by IDBI Bank, Canara Bank and other FI during 1993. The company is third credit rating agency being promoter, First being Crisil (Now owned by S&P) in 1987 and ICRA (Now owned by Moody’s) in 1991. Subsequently, 3 more companies, given Credit Rating license by SEBI which is India Rating (Owned by Fitch) in 1996, and Brickwork and SMERA which began rating business in 2008.
Source: ICICI Securities
Key financials:
http://www.screener.in/company/CARERATING/
Industry:
Over the past years, Regulation has played major role in development of rating business. In 1992, credit rating became mandatory for issuance of debt instrument with maturity/converability of 18 months and more. Subsequently, RBI guideline made rating mandatory for issuance of commercial paper and issue by public deposit by NBFCs.
In 2003, SEBI made rating mandatory for debt instruments placed under private placement basis and having maturity more than one year or more which were proposed to be listed. There was also regulation related to certain class of investors to invest not more than a stipulated part of their portfolio in unrated bonds.
Further with Basel II, RBI introduced a phased approach to adopt a “standarised approach” for credit risk, Under the standarised approach, RBI recognised certain credit rating agencies as eligible credit rating agencies and Indian banks were required to use such eligible credit rating agencies to access their credit risk in order to determine capital adequacy.
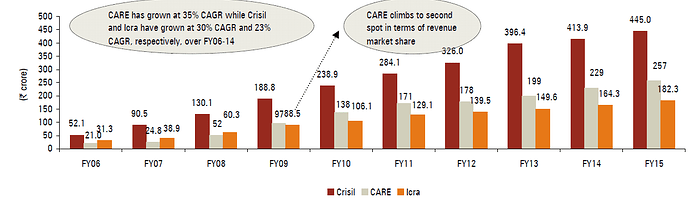
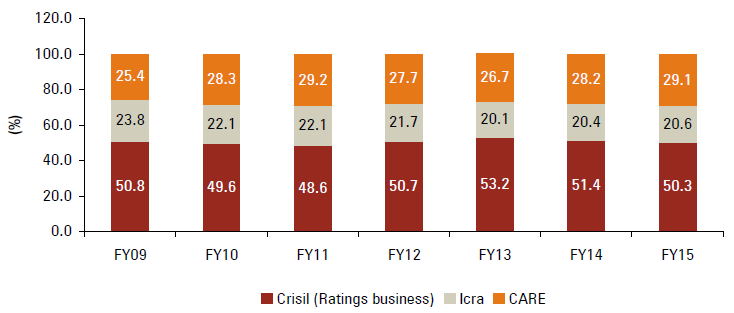
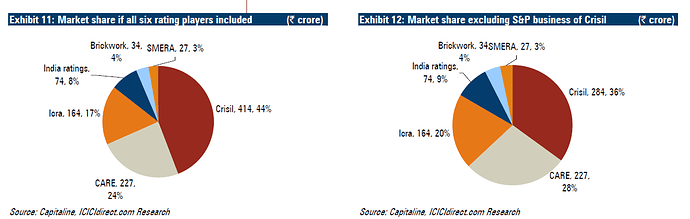
Past performance of CARE:
Source: ICICI Securities
Over last few years, CARE increases its market share as shown in image above. It has remained second largest player in Indian credit rating industry since FY2009.
Past Growth driver for CARE:
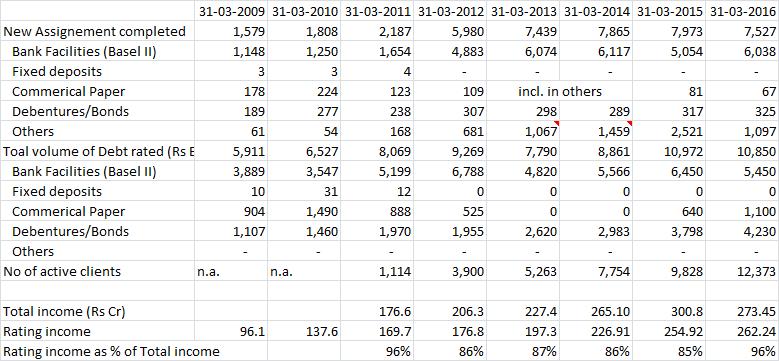
During last 7 years, Basel II driven Bank loan rating was a major growth driver for CARE. It is pertinent to note that while number of assignment has gone up at CAGR of 27% during FY09 to FY16 from Bank Facilities, in value term same growth is 8%. Debenture/Bond (assumed now shown as Long term instruments) has shown only CAGR growth of only 8% p.a. for no. of assignment, same has grown in value terms at CAGR of 21% p.a. Please note that FY09 to FY12 data was shown as Debenture/Bonds which are presented as Long term instrument from FY13 to FY16. The above analysis assumes that Debenture/Bonds are same as Long term instrument, and Commercial Paper is same as Short term instruments.
Future Prospect:
Corporate Bond Market: Future growth driver:
https://www.crisil.com/bond-market/pdf/Are-Stars-Aligning-for-Growth-of-Corporate-Bond-Market-in-India.pdf
The broad factor driving Indian bond market is very well explained in the document. Slide 15 in the presentation give major change in bond market.
Further, in above link, please refer to Page 38 which provides Indian Debt as per cent of GDP as against Global peer. India Corporate debt to GDP is around 17% of GDP as on Dec 31 2015 as against 20% of China, 123% of US, 44% of Malaysia. During 2010 to 2015, same has grown from 10.31% of GDP to 17% of GDP.
Risk Factors:
- Change in Management: CARE is undergoing a major change with Mr. Dogra retiring from the company from August 2016. Mr. Dogra has been associated with the company since inception. The new MD Mr. Rajesh Mokashi has also been associated with the company since inception. However, Mr. Dogra was very good marketer as per industry sources and one need to see how company manage this change in guard.
- High employee attrition: As per sources, the attrition in CARE is very high at entry level. The stable middle and Top management kind of provide stability to the operations, however, given the importance of manpower, the company face problem in case attrition rate continue to remain low. In case the company increase salary to align pay at entry level with its peer, then the operating margins which are highest among the credit rating players would likely to decline.
- Shift to Internal Rating Based Credit risk Approach: As explained earlier, implementation of BASEL II, was the main driver for rating revenue growth for the company. CARE derive around half of rating revenue from BLR segment as per brocker estimate, which is around 11% for Crisil and 25% for ICRA (broker estimate). In the event the bank opt for IRB, then CARE would have maximum problem among all industry players and also need to look at other segments to maintain its revenue and profitability.
- Regulatory risk: Approval from regulator has been key entry barrier in the industry. However, the recent defaults among emerging corporates with credit rating range from A- to BBB-, may adversely affect the performance of player. CARE is among large players in this segment and any regulatory adverse action would have major impact on the performance of the company.
Disclaimer:
I have recently purchased CARE shares in my portfolio and hence my views may be biased. The investor is requested to do its own due diligence before taking any investment decision.